
Jones fractures are caused by overuse, repetitive stress, or trauma. A Jones fracture can be either a stress fracture (a tiny hairline break that occurs over time) or an acute (sudden) break. Jones fractures occur in a small area of the fifth metatarsal that receives less blood and is therefore more prone to difficulties in healing. Avulsion fractures are often overlooked when they occur with an ankle sprain. This type of fracture is the result of an injury in which the ankle rolls. In an avulsion fracture, a small piece of bone is pulled off the main portion of the bone by a tendon or ligament.
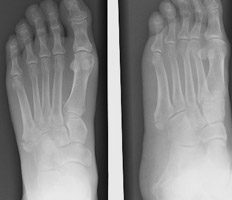
Two types of fractures that often occur in the fifth metatarsal are: This document can be made available in alternative formats on request for a person with a disability.Fractures (breaks) are common in the fifth metatarsal – the long bone on the outside of the foot that connects to the little toe. Kluwer W, Rang's Children's Fractures Fourth edition.
#JONES FRACTURE FOOT TRIAL#
Randomised controlled trial comparing immobilisation in above-knee plaster of Paris to controlled ankle motion boots in undisplaced paediatric spiral tibial fractures. Bradman K, Stannage K, O’Brien S, Green, S et al.Relocate and buddy strap with no specific follow up.Buddy strap and Darco walking shoe or sturdy shoes with no specific follow up.Consider reduction if significantly angulated.Other phalangeal fractures (including distal phalangeal fractures of the big / 1st toe)Īngulated Salter-Harris II fracture of 5th proximal phalanxĭorsally displaced transverse fracture of neck of 3rd proximal phalanx Darco Shoe non-weight bearing with crutches and follow up in Fracture Clinic in 1 week.Phalangeal (Toe) Fractures Open and intra-articular fractures These intra-articular fractures are managed in a below knee backslab non weight bearing with crutches and Fracture clinic follow-up in 1 week. It is important to differentiate avulsion fractures of the base of the fifth metatarsal with Jones fractures which involve the 4th and 5th inter-metatarsal joint.CAM boot weight bearing as tolerated with Fracture Clinic follow up in 1 week.1Īvulsion fracture at the base of the fifth metatarsal (insertion of peroneus brevis)įracture of base of 5th metatarsal follow inversion injury Minimally displaced oblique of the 5th metatarsal Metatarsal fractures Undisplaced metatarsal fractures 1 Tarsometatarsal fractures (Lisfranc disruption) Avulsion fractures of the navicular or cuboid Controlled Ankle Motion (CAM) boot weight bearing as tolerated with GP follow up in 7-10 days. Midfoot fracturesīe wary of compartment syndrome in major midfoot fractures.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/x-ray-image-of-bone-fracture-at-5th-metatarsal-left-foot-945203958-140a7bb8add94610838f0b3632543a5c.jpg)
Talar dome fracture – looks simple on plain X-ray but CT shows multiple intra-articular bony fragments.

Refer to Orthopaedic team (high risk of avascular necrosis).A CT scan may be indicated in talar fractures, intra-articular calcaneal fractures, severe crush injuries or suspicion of Lisfranc injury.įor general assessment and management, see Fractures - Overview.If the calcaneus is tender, dedicated axial calcaneal views must be requested as calcaneal fractures may not be visible on standard views.If there is midfoot tenderness, look carefully at the joint between the medial cuneiform and 2nd metatarsal base for a Lisfranc fracture as findings can be subtle.A foot X-ray should have dorsopalmar, oblique and lateral views.Localised pain, swelling and tenderness with reluctance to weight bear.In these cases, compression fractures of the spine should also be considered. Calcaneal fractures occur after a fall from a height landing on the heels.Tarsal fractures are uncommon in isolation and are usually seen in crush injuries.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/x-ray-image-of-bone-fracture-at-5th-metatarsal-left-foot-945203958-140a7bb8add94610838f0b3632543a5c.jpg)
Crush injuries, stubbing of toes, kicking and tripping.Clinicians should also consider the local skill level available and their local area policies before following any guideline. These clinical guidelines should never be relied on as a substitute for proper assessment with respect to the particular circumstances of each case and the needs of each patient. Clinical common-sense should be applied at all times. They are not strict protocols, and they do not replace the judgement of a senior clinician. These guidelines have been produced to guide clinical decision making for the medical, nursing and allied health staff of Perth Children’s Hospital.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
